The Rising Epidemic of Preventable Fatty Liver Disease
The Rising Epidemic of Preventable Fatty Liver Disease
Introduction
In the fast-paced world we inhabit, our dietary choices hold immense sway over our overall health. It is imperative to be cognizant of what we consume and abstain from, as certain lifestyle factors contribute to the escalating prevalence of preventable liver diseases, particularly nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
Understanding Fatty Liver Disease
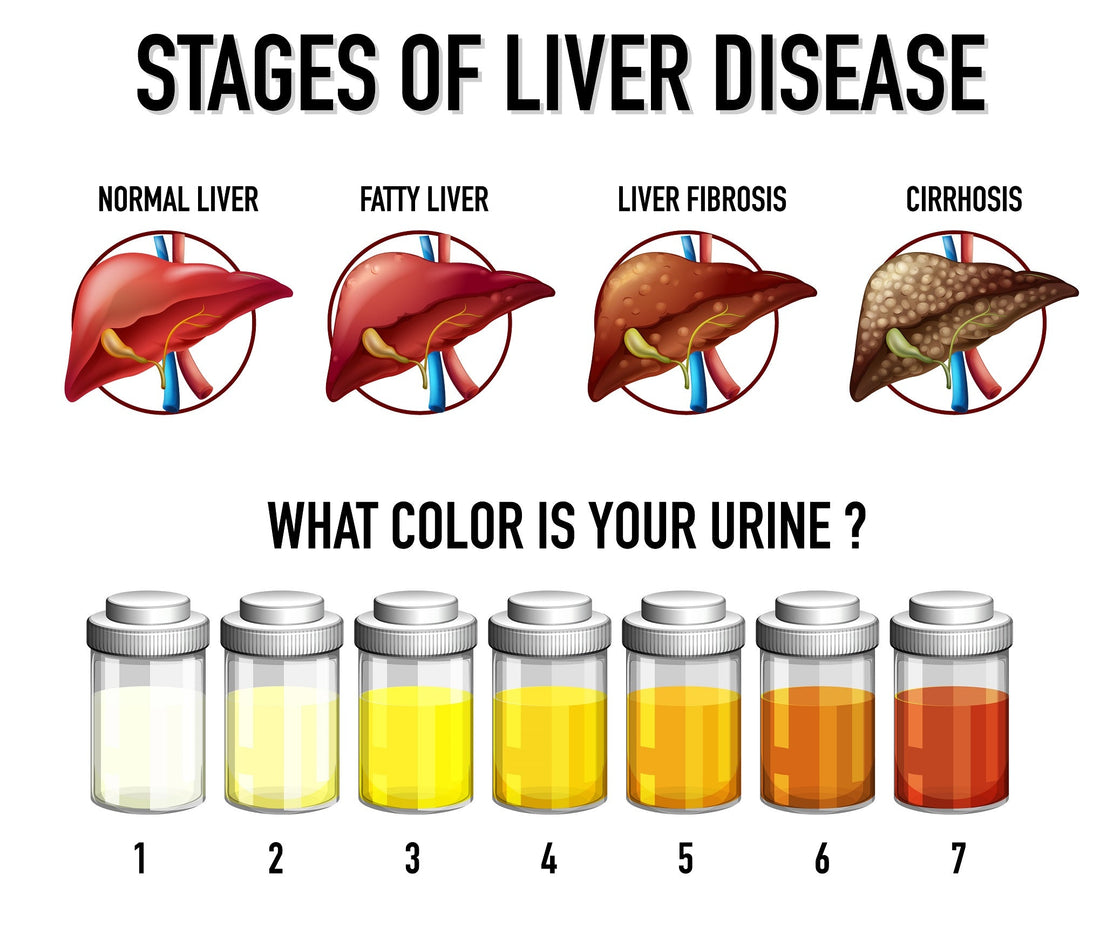
Fatty liver disease, also referred to as hepatic steatosis, manifests as an excessive accumulation of fat within liver cells. This condition can arise from various factors, including obesity, excessive alcohol consumption, or certain medications. As time elapses, fatty liver disease can incite liver inflammation and scarring, leading to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and potentially progressing to more severe liver ailments such as cirrhosis and liver cancer. The ramifications of these deleterious consequences extend to our overall well-being, influencing liver function, metabolic processes, and overall health. Timely intervention through lifestyle modifications and medical treatments is paramount to mitigate the adverse effects of fatty liver disease.
1. Differentiating NAFLD Caused by Lifestyle Factors and Other Etiologies
When examining non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) caused by lifestyle factors, it exhibits characteristic associations with obesity, insulin resistance, and metabolic syndrome. Conversely, other etiologies of fatty liver disease encompass alcohol-induced liver disease (ALD), viral hepatitis, autoimmune liver diseases, certain medications, and genetic disorders. Accurate differentiation among these diverse causes is essential for precise diagnosis and the implementation of tailored management strategies, as specific interventions and treatments may be required.
2. Metabolic Risk Factors and the Development of NAFLD
Metabolic risk factors intricately entwined with the development of NAFLD include obesity, particularly abdominal adiposity, which releases inflammatory substances that foster liver fat accumulation. Insulin resistance, a defining feature of metabolic syndrome, significantly impairs the liver's ability to process and store fats effectively. Dyslipidemia, characterized by elevated triglyceride levels and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, further contributes to the progression of NAFLD. Additionally, conditions such as type 2 diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and polycystic ovary syndrome heighten the risk of NAFLD. These interplaying metabolic risk factors create an environment conducive to hepatic fat accumulation and the subsequent advancement of NAFLD. It is of utmost importance to address and manage these risk factors diligently to mitigate their impact on liver health and overall well-being.
3. Emphasizing the Profound Impact of Our Dietary Choices on Metabolic Health and Liver Function
Our dietary choices play a crucial role in shaping our metabolic health and liver function. The foods we consume can either promote or hinder the development and progression of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
A. The Significance of a Nutrient-Rich Diet
A diet rich in essential nutrients, including vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, is vital for optimal metabolic health and liver function. Nutrient deficiencies can impair liver function and contribute to the progression of NAFLD. Emphasizing the consumption of whole foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats, can provide the necessary nutrients to support liver health.
B. The Detrimental Effects of Excessive Sugar and Processed Foods
Excessive consumption of added sugars and processed foods has been strongly linked to the development of NAFLD. These foods are often high in fructose, which can lead to increased fat accumulation in the liver and contribute to insulin resistance. Raising awareness about the detrimental effects of these dietary factors is essential in preventing and managing NAFLD.
4. Advocating for the Adoption of Healthful Eating Patterns
Adopting healthful eating patterns can significantly reduce the risk of developing NAFLD. The Mediterranean diet, renowned for its health benefits, has shown promise in preventing and managing this condition. Promoting the adoption of such dietary patterns can have a positive impact on liver health.
A. The Mediterranean Diet and Its Benefits
The Mediterranean diet is characterized by a high consumption of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, seeds, olive oil, and moderate intake of fish, poultry, and dairy. This dietary pattern is rich in anti-inflammatory compounds, antioxidants, and healthy fats, which can support liver health and reduce the risk of NAFLD.
B. The Role of the Mediterranean Diet in NAFLD Prevention
Research suggests that adherence to the Mediterranean diet is associated with a lower prevalence of NAFLD and a reduced risk of disease progression. The combination of plant-based foods, healthy fats, and limited intake of processed foods aligns with the nutritional needs to prevent liver fat accumulation and promote overall metabolic health.
5. Educating Individuals about the Indispensable Role of Weight Management and Physical Activity in Mitigating the Risk of NAFLD
Weight management and regular physical activity are essential components in mitigating the risk of developing NAFLD. Educating individuals about the significance of maintaining a healthy weight and engaging in regular exercise is crucial for the prevention and management of this condition.
A. The Impact of Excess Weight on Liver Health
Excess weight, particularly abdominal adiposity, is strongly associated with NAFLD. It contributes to insulin resistance, inflammation, and fat accumulation in the liver. Understanding the detrimental effects of excess weight on liver health can motivate individuals to prioritize weight management as a preventive measure.
B. Regular Physical Activity and Its Benefits for Liver Health
Engaging in regular physical activity has numerous benefits for liver health. Exercise helps improve insulin sensitivity, aids in weight management, and reduces inflammation. Encouraging individuals to incorporate regular physical activity into their daily routine can significantly reduce the risk of NAFLD and improve overall metabolic health.
6. Foods and Beverages to Avoid
The Pernicious Effects of Regular Fast Food Consumption on Liver Health
Regular consumption of fast food has become increasingly common in our modern society. However, it is crucial to shed light on the detrimental effects that this dietary habit can have on liver health, particularly in relation to the development and progression of fatty liver disease.
A. The High Fat and Calorie Content of Fast Food
Fast food is often high in unhealthy fats and calories, which can contribute to weight gain and obesity. Excessive calorie intake, especially from unhealthy sources, can lead to liver fat accumulation and increase the risk of developing non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
B. Sodium and Trans Fat Content
Fast food is notorious for its high sodium and trans fat content. Excessive sodium intake can lead to fluid retention and liver inflammation, while trans fats are known to promote inflammation and insulin resistance, both of which are detrimental to liver health.
7. The Detrimental Consequences of High-Fructose Corn Syrup and Sugar-Sweetened Beverages, which Contribute to Liver Fat Accumulation
The consumption of high-fructose corn syrup (HFCS) and sugar-sweetened beverages has become pervasive in our modern diet. Raising awareness about their detrimental consequences on liver health is imperative in combating the rising prevalence of fatty liver disease.
A. The Role of High-Fructose Corn Syrup
HFCS, commonly used as a sweetener in processed foods and beverages, can have detrimental effects on liver health. Excessive fructose consumption overwhelms the liver's capacity to metabolize it, leading to increased fat production and liver fat accumulation. This process contributes to the development and progression of NAFLD.
B. Sugar-Sweetened Beverages and Liver Fat Accumulation
Sugar-sweetened beverages, such as sodas and energy drinks, are major contributors to excessive sugar intake. These beverages contain high amounts of added sugars, primarily in the form of fructose. Regular consumption of sugar-sweetened beverages has been strongly associated with increased liver fat accumulation and a higher risk of developing NAFLD.
8. Association between Alcohol Consumption, Liver Damage, and the Development of Fatty Liver Disease
Alcohol consumption has long been recognized as a significant contributor to liver damage and the development of alcoholic fatty liver disease (AFLD). Understanding the association between alcohol consumption and fatty liver disease is crucial for raising awareness and promoting responsible alcohol consumption.
A. The Effects of Alcohol on Liver Function
Alcohol is metabolized by the liver, and excessive alcohol consumption can overwhelm the liver's capacity to process it. This leads to the accumulation of fat in liver cells, inflammation, and liver damage. Prolonged alcohol abuse can progress to more severe liver conditions, such as alcoholic hepatitis and cirrhosis.
B. Differentiating Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) from Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (AFLD)
While NAFLD is primarily associated with lifestyle factors, AFLD specifically stems from excessive alcohol consumption. It is important to differentiate between the two conditions, as they may require different approaches to management and treatment.
9. Foods to Embrace for a Healthy Liver
The foods we consume have a profound impact on liver health. By incorporating nutrient-rich whole foods, healthy fats, and certain beverages into our diet, we can actively support and fortify the health of our liver.
A. The Benefits of Whole Foods
Whole foods, such as vegetables, berries, eggs, poultry, and nuts, offer a plethora of essential nutrients that promote liver health. Vegetables, particularly leafy greens, are rich in antioxidants and fiber, aiding in detoxification and reducing inflammation. Berries provide a range of protective compounds that support liver function. Eggs and poultry are excellent sources of high-quality protein, aiding in the repair and regeneration of liver cells. Nuts contain beneficial fats, antioxidants, and other nutrients that contribute to overall liver health.
B. Incorporating Healthy Fats
Healthy fats, such as monounsaturated fats found in olive oil and avocados, play a vital role in maintaining liver health. These fats help reduce inflammation and promote healthy cholesterol levels. Including these sources of healthy fats in our daily food choices can provide the necessary building blocks for optimal liver function.
C. The Potential Benefits of Coffee and Green Tea
Research suggests that both coffee and green tea may have positive effects on liver health. Coffee consumption has been associated with a decreased risk of liver diseases, including cirrhosis and liver cancer. It exhibits antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, as well as enhancing liver enzyme levels. Green tea, rich in antioxidants called catechins, has shown potential in preventing liver fat accumulation and reducing the risk of liver diseases. Incorporating moderate amounts of coffee and green tea into our routine may contribute to a healthier liver.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the prevention and reversal of preventable liver diseases, such as NAFLD, require our utmost attention. Fortunately, we have the power to combat these conditions through mindful dietary interventions. By making conscientious food choices, avoiding harmful substances, and embracing healthful eating patterns like the esteemed Mediterranean diet, we can significantly reduce our vulnerability to fatty liver disease. Nurturing our livers with a diet rich in whole foods, abundant in vital nutrients, holds the promise of securing a healthier future. Let us remember to prioritize the care and nourishment of our livers by empowering them with the right foods and beverages on our journey towards wellness. It is important to emphasize that maintaining a balanced diet and seeking personalized dietary advice from healthcare professionals are essential in optimizing liver health.
Note: This blog article draws upon the information provided in the source URL and is intended to furnish general knowledge and suggestions. It is prudent to consult healthcare professionals for personalized advice and guidance pertaining to specific health concerns.
Sources:
1. Fatty Liver Disease
2. Fatty liver
3. 10 Foods to Include in a Healthy Liver Diet
Introduction
In the fast-paced world we inhabit, our dietary choices hold immense sway over our overall health. It is imperative to be cognizant of what we consume and abstain from, as certain lifestyle factors contribute to the escalating prevalence of preventable liver diseases, particularly nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
Understanding Fatty Liver Disease
Fatty liver disease, also referred to as hepatic steatosis, manifests as an excessive accumulation of fat within liver cells. This condition can arise from various factors, including obesity, excessive alcohol consumption, or certain medications. As time elapses, fatty liver disease can incite liver inflammation and scarring, leading to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and potentially progressing to more severe liver ailments such as cirrhosis and liver cancer. The ramifications of these deleterious consequences extend to our overall well-being, influencing liver function, metabolic processes, and overall health. Timely intervention through lifestyle modifications and medical treatments is paramount to mitigate the adverse effects of fatty liver disease.
1. Differentiating NAFLD Caused by Lifestyle Factors and Other Etiologies
When examining non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) caused by lifestyle factors, it exhibits characteristic associations with obesity, insulin resistance, and metabolic syndrome. Conversely, other etiologies of fatty liver disease encompass alcohol-induced liver disease (ALD), viral hepatitis, autoimmune liver diseases, certain medications, and genetic disorders. Accurate differentiation among these diverse causes is essential for precise diagnosis and the implementation of tailored management strategies, as specific interventions and treatments may be required.
2. Metabolic Risk Factors and the Development of NAFLD
Metabolic risk factors intricately entwined with the development of NAFLD include obesity, particularly abdominal adiposity, which releases inflammatory substances that foster liver fat accumulation. Insulin resistance, a defining feature of metabolic syndrome, significantly impairs the liver's ability to process and store fats effectively. Dyslipidemia, characterized by elevated triglyceride levels and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, further contributes to the progression of NAFLD. Additionally, conditions such as type 2 diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and polycystic ovary syndrome heighten the risk of NAFLD. These interplaying metabolic risk factors create an environment conducive to hepatic fat accumulation and the subsequent advancement of NAFLD. It is of utmost importance to address and manage these risk factors diligently to mitigate their impact on liver health and overall well-being.
3. Emphasizing the Profound Impact of Our Dietary Choices on Metabolic Health and Liver Function
Our dietary choices play a crucial role in shaping our metabolic health and liver function. The foods we consume can either promote or hinder the development and progression of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
A. The Significance of a Nutrient-Rich Diet
A diet rich in essential nutrients, including vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, is vital for optimal metabolic health and liver function. Nutrient deficiencies can impair liver function and contribute to the progression of NAFLD. Emphasizing the consumption of whole foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats, can provide the necessary nutrients to support liver health.
B. The Detrimental Effects of Excessive Sugar and Processed Foods
Excessive consumption of added sugars and processed foods has been strongly linked to the development of NAFLD. These foods are often high in fructose, which can lead to increased fat accumulation in the liver and contribute to insulin resistance. Raising awareness about the detrimental effects of these dietary factors is essential in preventing and managing NAFLD.
4. Advocating for the Adoption of Healthful Eating Patterns
Adopting healthful eating patterns can significantly reduce the risk of developing NAFLD. The Mediterranean diet, renowned for its health benefits, has shown promise in preventing and managing this condition. Promoting the adoption of such dietary patterns can have a positive impact on liver health.
A. The Mediterranean Diet and Its Benefits
The Mediterranean diet is characterized by a high consumption of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, seeds, olive oil, and moderate intake of fish, poultry, and dairy. This dietary pattern is rich in anti-inflammatory compounds, antioxidants, and healthy fats, which can support liver health and reduce the risk of NAFLD.
B. The Role of the Mediterranean Diet in NAFLD Prevention
Research suggests that adherence to the Mediterranean diet is associated with a lower prevalence of NAFLD and a reduced risk of disease progression. The combination of plant-based foods, healthy fats, and limited intake of processed foods aligns with the nutritional needs to prevent liver fat accumulation and promote overall metabolic health.
5. Educating Individuals about the Indispensable Role of Weight Management and Physical Activity in Mitigating the Risk of NAFLD
Weight management and regular physical activity are essential components in mitigating the risk of developing NAFLD. Educating individuals about the significance of maintaining a healthy weight and engaging in regular exercise is crucial for the prevention and management of this condition.
A. The Impact of Excess Weight on Liver Health
Excess weight, particularly abdominal adiposity, is strongly associated with NAFLD. It contributes to insulin resistance, inflammation, and fat accumulation in the liver. Understanding the detrimental effects of excess weight on liver health can motivate individuals to prioritize weight management as a preventive measure.
B. Regular Physical Activity and Its Benefits for Liver Health
Engaging in regular physical activity has numerous benefits for liver health. Exercise helps improve insulin sensitivity, aids in weight management, and reduces inflammation. Encouraging individuals to incorporate regular physical activity into their daily routine can significantly reduce the risk of NAFLD and improve overall metabolic health.
6. Foods and Beverages to Avoid
The Pernicious Effects of Regular Fast Food Consumption on Liver Health
Regular consumption of fast food has become increasingly common in our modern society. However, it is crucial to shed light on the detrimental effects that this dietary habit can have on liver health, particularly in relation to the development and progression of fatty liver disease.
A. The High Fat and Calorie Content of Fast Food
Fast food is often high in unhealthy fats and calories, which can contribute to weight gain and obesity. Excessive calorie intake, especially from unhealthy sources, can lead to liver fat accumulation and increase the risk of developing non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
B. Sodium and Trans Fat Content
Fast food is notorious for its high sodium and trans fat content. Excessive sodium intake can lead to fluid retention and liver inflammation, while trans fats are known to promote inflammation and insulin resistance, both of which are detrimental to liver health.
7. The Detrimental Consequences of High-Fructose Corn Syrup and Sugar-Sweetened Beverages, which Contribute to Liver Fat Accumulation
The consumption of high-fructose corn syrup (HFCS) and sugar-sweetened beverages has become pervasive in our modern diet. Raising awareness about their detrimental consequences on liver health is imperative in combating the rising prevalence of fatty liver disease.
A. The Role of High-Fructose Corn Syrup
HFCS, commonly used as a sweetener in processed foods and beverages, can have detrimental effects on liver health. Excessive fructose consumption overwhelms the liver's capacity to metabolize it, leading to increased fat production and liver fat accumulation. This process contributes to the development and progression of NAFLD.
B. Sugar-Sweetened Beverages and Liver Fat Accumulation
Sugar-sweetened beverages, such as sodas and energy drinks, are major contributors to excessive sugar intake. These beverages contain high amounts of added sugars, primarily in the form of fructose. Regular consumption of sugar-sweetened beverages has been strongly associated with increased liver fat accumulation and a higher risk of developing NAFLD.
8. Association between Alcohol Consumption, Liver Damage, and the Development of Fatty Liver Disease
Alcohol consumption has long been recognized as a significant contributor to liver damage and the development of alcoholic fatty liver disease (AFLD). Understanding the association between alcohol consumption and fatty liver disease is crucial for raising awareness and promoting responsible alcohol consumption.
A. The Effects of Alcohol on Liver Function
Alcohol is metabolized by the liver, and excessive alcohol consumption can overwhelm the liver's capacity to process it. This leads to the accumulation of fat in liver cells, inflammation, and liver damage. Prolonged alcohol abuse can progress to more severe liver conditions, such as alcoholic hepatitis and cirrhosis.
B. Differentiating Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) from Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (AFLD)
While NAFLD is primarily associated with lifestyle factors, AFLD specifically stems from excessive alcohol consumption. It is important to differentiate between the two conditions, as they may require different approaches to management and treatment.
9. Foods to Embrace for a Healthy Liver
The foods we consume have a profound impact on liver health. By incorporating nutrient-rich whole foods, healthy fats, and certain beverages into our diet, we can actively support and fortify the health of our liver.
A. The Benefits of Whole Foods
Whole foods, such as vegetables, berries, eggs, poultry, and nuts, offer a plethora of essential nutrients that promote liver health. Vegetables, particularly leafy greens, are rich in antioxidants and fiber, aiding in detoxification and reducing inflammation. Berries provide a range of protective compounds that support liver function. Eggs and poultry are excellent sources of high-quality protein, aiding in the repair and regeneration of liver cells. Nuts contain beneficial fats, antioxidants, and other nutrients that contribute to overall liver health.
B. Incorporating Healthy Fats
Healthy fats, such as monounsaturated fats found in olive oil and avocados, play a vital role in maintaining liver health. These fats help reduce inflammation and promote healthy cholesterol levels. Including these sources of healthy fats in our daily food choices can provide the necessary building blocks for optimal liver function.
C. The Potential Benefits of Coffee and Green Tea
Research suggests that both coffee and green tea may have positive effects on liver health. Coffee consumption has been associated with a decreased risk of liver diseases, including cirrhosis and liver cancer. It exhibits antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, as well as enhancing liver enzyme levels. Green tea, rich in antioxidants called catechins, has shown potential in preventing liver fat accumulation and reducing the risk of liver diseases. Incorporating moderate amounts of coffee and green tea into our routine may contribute to a healthier liver.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the prevention and reversal of preventable liver diseases, such as NAFLD, require our utmost attention. Fortunately, we have the power to combat these conditions through mindful dietary interventions. By making conscientious food choices, avoiding harmful substances, and embracing healthful eating patterns like the esteemed Mediterranean diet, we can significantly reduce our vulnerability to fatty liver disease. Nurturing our livers with a diet rich in whole foods, abundant in vital nutrients, holds the promise of securing a healthier future. Let us remember to prioritize the care and nourishment of our livers by empowering them with the right foods and beverages on our journey towards wellness. It is important to emphasize that maintaining a balanced diet and seeking personalized dietary advice from healthcare professionals are essential in optimizing liver health.
Note: This blog article draws upon the information provided in the source URL and is intended to furnish general knowledge and suggestions. It is prudent to consult healthcare professionals for personalized advice and guidance pertaining to specific health concerns.
Sources:
1. Fatty Liver Disease
2. Fatty liver
3. 10 Foods to Include in a Healthy Liver Diet