Warts
Warts
Causes, Types, Treatments, and Prevention Explained
Introduction
Warts are a common skin infection caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV). They appear as rough, skin-colored bumps on the skin and can affect various parts of the body, including the hands, feet, face, genitals, and knees.
Causes and Types of Warts
Warts are caused by the HPV virus, which enters the skin through cuts or breaks and leads to an infection. While anyone can get warts, children are more prone to them due to their increased likelihood of getting cuts. People with weakened immune systems, such as those with autoimmune diseases or the elderly, are also more susceptible to the virus.
Different types of warts
1. Common Warts: These are the most frequently occurring warts and usually appear on the hands.
2. Flat Warts: These warts are flat and typically affect the face and forehead.
3. Plantar Warts: These warts develop on the soles of the feet and can be painful. They often resemble calluses with small black dots in the center.
4. Genital Warts: These warts form on the penis, vagina, or rectum and are sexually transmitted. It is essential to practice safe sex and get the HPV vaccine to prevent genital warts.
5. Periungual and Subungual Warts: These warts appear around or under the fingernails and toenails.
Treatment Options
While warts can often go away on their own as the immune system fights off the virus, treatment may be necessary to prevent their spread, alleviate discomfort, or address cosmetic concerns.
Here are some common treatment options:
1. At-home Wart Removal
Over-the-counter wart removal medications containing salicylic acid can gradually dissolve warts layer by layer. These products come in liquid, gel, or patch form and require daily application for several months.
2. Freezing (Cryotherapy)
Liquid nitrogen is applied to the wart, freezing it and causing a blister to form. The blister and wart eventually peel off. Multiple cryotherapy treatments may be necessary.
3. Immunotherapy
This treatment is used for stubborn warts that do not respond to traditional methods. It involves applying a topical chemical, such as diphencyprone (DCP), which triggers a mild allergic reaction, ultimately eliminating the wart.
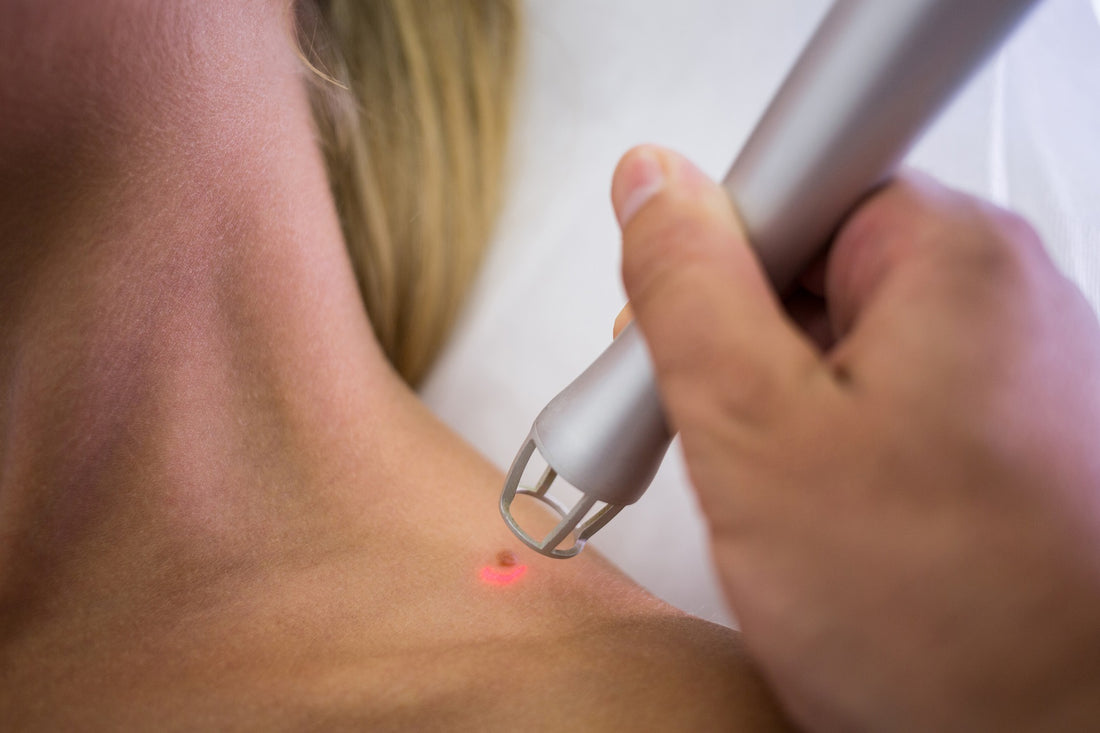
4. Laser Treatment
Laser light is used to heat and destroy the blood vessels inside the wart, cutting off its blood supply and causing it to die.
5. Topical Medicine
A liquid mixture containing cantharidin, a chemical, is applied to the wart. A blister forms underneath and cuts off the wart's blood supply. The dead wart is then removed by a healthcare professional.
Benefits and Side Effects of Treatment
The primary benefit of wart treatment is the removal of warts, which can be unsightly, cause discomfort, or lead to self-consciousness. By eliminating warts, treatment also reduces the risk of complications such as cancer (linked to HPV and genital warts), disfigurement, infection, and pain.
Some potential side effects that can be expective from the common treatment options mentioned above:
1. At-home Wart Removal
Skin irritation, redness, and peeling may occur with salicylic acid-based products.
2. Freezing (Cryotherapy)
After the procedure, blistering, swelling, and temporary pain or discomfort at the treatment site are common.
3. Immunotherapy
Allergic reactions, such as redness, itching, and skin inflammation, can occur.
4. Laser Treatment
Possible side effects include temporary pain, swelling, redness, and scarring.
5. Topical Medicine
The application of cantharidin may cause pain, burning, blistering, or skin irritation.
Prevention
While it is challenging to completely prevent warts, you can take certain steps to reduce the risk of getting or spreading them:
- Avoid shaving over a wart.
- Break the habit of biting nails or picking at cuticles.
- Refrain from sharing personal items like towels, clothing, nail clippers, etc.
- Avoid touching another person's wart.
- Receive the HPV vaccine and practice safe sex to prevent genital warts.
- Keep your feet dry to prevent the spread of plantar warts.
- Avoid scratching, cutting, or picking at a wart.
- Wear flip-flops or shoes when using public locker rooms, pool areas, or showers.
Conclusion
Warts, caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV), are common skin infections that can appear on various parts of the body. While they often go away on their own, treatment may be necessary in certain cases. Treatment options range from at-homewart removal to medical interventions like cryotherapy, immunotherapy, laser treatment, and topical medicine. Each treatment option has its benefits and potential side effects, which should be considered when making a decision.
Prevention of warts involves practicing good hygiene, avoiding direct contact with warts, getting vaccinated against HPV, and taking precautions during sexual activity.
Remember, if you have concerns about warts or any skin condition, it is always best to consult with a healthcare professional who can provide a proper diagnosis and recommend the most suitable treatment option for your specific situation.
Sources:
1. Genital HPV Infection – Basic Fact Sheet
2. How Do I Know if I Have Genital Warts?
3. What are the symptoms of HPV?
Causes, Types, Treatments, and Prevention Explained
Introduction
Warts are a common skin infection caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV). They appear as rough, skin-colored bumps on the skin and can affect various parts of the body, including the hands, feet, face, genitals, and knees.
Causes and Types of Warts
Warts are caused by the HPV virus, which enters the skin through cuts or breaks and leads to an infection. While anyone can get warts, children are more prone to them due to their increased likelihood of getting cuts. People with weakened immune systems, such as those with autoimmune diseases or the elderly, are also more susceptible to the virus.
Different types of warts
1. Common Warts: These are the most frequently occurring warts and usually appear on the hands.
2. Flat Warts: These warts are flat and typically affect the face and forehead.
3. Plantar Warts: These warts develop on the soles of the feet and can be painful. They often resemble calluses with small black dots in the center.
4. Genital Warts: These warts form on the penis, vagina, or rectum and are sexually transmitted. It is essential to practice safe sex and get the HPV vaccine to prevent genital warts.
5. Periungual and Subungual Warts: These warts appear around or under the fingernails and toenails.
Treatment Options
While warts can often go away on their own as the immune system fights off the virus, treatment may be necessary to prevent their spread, alleviate discomfort, or address cosmetic concerns.
Here are some common treatment options:
1. At-home Wart Removal
Over-the-counter wart removal medications containing salicylic acid can gradually dissolve warts layer by layer. These products come in liquid, gel, or patch form and require daily application for several months.
2. Freezing (Cryotherapy)
Liquid nitrogen is applied to the wart, freezing it and causing a blister to form. The blister and wart eventually peel off. Multiple cryotherapy treatments may be necessary.
3. Immunotherapy
This treatment is used for stubborn warts that do not respond to traditional methods. It involves applying a topical chemical, such as diphencyprone (DCP), which triggers a mild allergic reaction, ultimately eliminating the wart.
4. Laser Treatment
Laser light is used to heat and destroy the blood vessels inside the wart, cutting off its blood supply and causing it to die.
5. Topical Medicine
A liquid mixture containing cantharidin, a chemical, is applied to the wart. A blister forms underneath and cuts off the wart's blood supply. The dead wart is then removed by a healthcare professional.
Benefits and Side Effects of Treatment
The primary benefit of wart treatment is the removal of warts, which can be unsightly, cause discomfort, or lead to self-consciousness. By eliminating warts, treatment also reduces the risk of complications such as cancer (linked to HPV and genital warts), disfigurement, infection, and pain.
Some potential side effects that can be expective from the common treatment options mentioned above:
1. At-home Wart Removal
Skin irritation, redness, and peeling may occur with salicylic acid-based products.
2. Freezing (Cryotherapy)
After the procedure, blistering, swelling, and temporary pain or discomfort at the treatment site are common.
3. Immunotherapy
Allergic reactions, such as redness, itching, and skin inflammation, can occur.
4. Laser Treatment
Possible side effects include temporary pain, swelling, redness, and scarring.
5. Topical Medicine
The application of cantharidin may cause pain, burning, blistering, or skin irritation.
Prevention
While it is challenging to completely prevent warts, you can take certain steps to reduce the risk of getting or spreading them:
- Avoid shaving over a wart.
- Break the habit of biting nails or picking at cuticles.
- Refrain from sharing personal items like towels, clothing, nail clippers, etc.
- Avoid touching another person's wart.
- Receive the HPV vaccine and practice safe sex to prevent genital warts.
- Keep your feet dry to prevent the spread of plantar warts.
- Avoid scratching, cutting, or picking at a wart.
- Wear flip-flops or shoes when using public locker rooms, pool areas, or showers.
Conclusion
Warts, caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV), are common skin infections that can appear on various parts of the body. While they often go away on their own, treatment may be necessary in certain cases. Treatment options range from at-homewart removal to medical interventions like cryotherapy, immunotherapy, laser treatment, and topical medicine. Each treatment option has its benefits and potential side effects, which should be considered when making a decision.
Prevention of warts involves practicing good hygiene, avoiding direct contact with warts, getting vaccinated against HPV, and taking precautions during sexual activity.
Remember, if you have concerns about warts or any skin condition, it is always best to consult with a healthcare professional who can provide a proper diagnosis and recommend the most suitable treatment option for your specific situation.
Sources:
1. Genital HPV Infection – Basic Fact Sheet
2. How Do I Know if I Have Genital Warts?
3. What are the symptoms of HPV?